Brick manufacturing has been an essential part of construction for centuries, providing durable and aesthetically pleasing building materials. However, the process of producing bricks is not without its challenges. As the world becomes more environmentally conscious and construction practices evolve, it is crucial to examine the problems associated with brick manufacturing. This article will explore the environmental impact, resource depletion, labor issues, technological challenges, and market fluctuations that affect the brick industry.
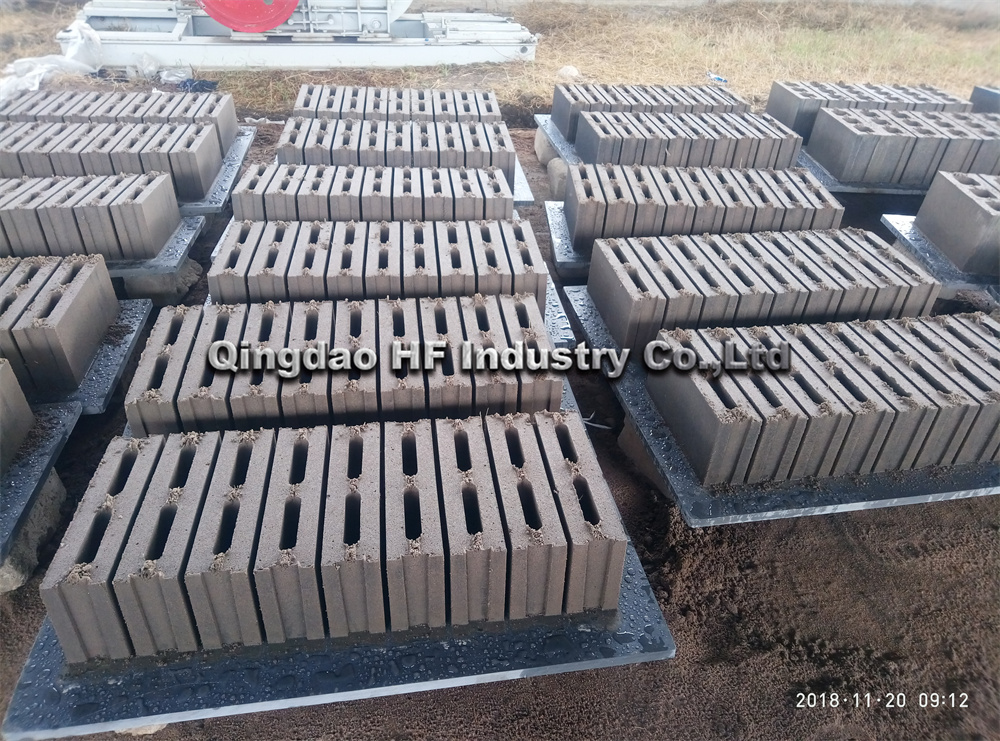

One of the most significant problems with brick manufacturing is its environmental impact. Traditional brick production involves the extraction of clay and other natural materials, which can lead to habitat destruction and soil degradation. The mining process often disrupts local ecosystems, affecting flora and fauna and leading to a loss of biodiversity.

One of the most significant environmental issues with brick manufacturing is air pollution. Traditional brick kilns, especially those in developing countries, often use low-quality fuels like coal, wood, and agricultural waste. The combustion of these fuels releases a myriad of pollutants, including sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO). These emissions contribute to air quality deterioration, smog formation, and respiratory illnesses among nearby populations.

The extraction of raw materials for brick manufacturing poses a significant risk of resource depletion. Clay, sand, and other materials are finite resources, and their over-extraction can lead to shortages. As urbanization and construction continue to rise, the demand for bricks increases, putting pressure on these natural resources.
In addition, the geographic distribution of clay deposits is uneven, leading to transportation challenges and increased costs. Regions with abundant clay may not be near major construction markets, necessitating long-distance transportation that further exacerbates environmental concerns. Sustainable practices, such as recycling old bricks or using alternative materials, are essential to mitigate these issues, but they are not yet widely adopted.
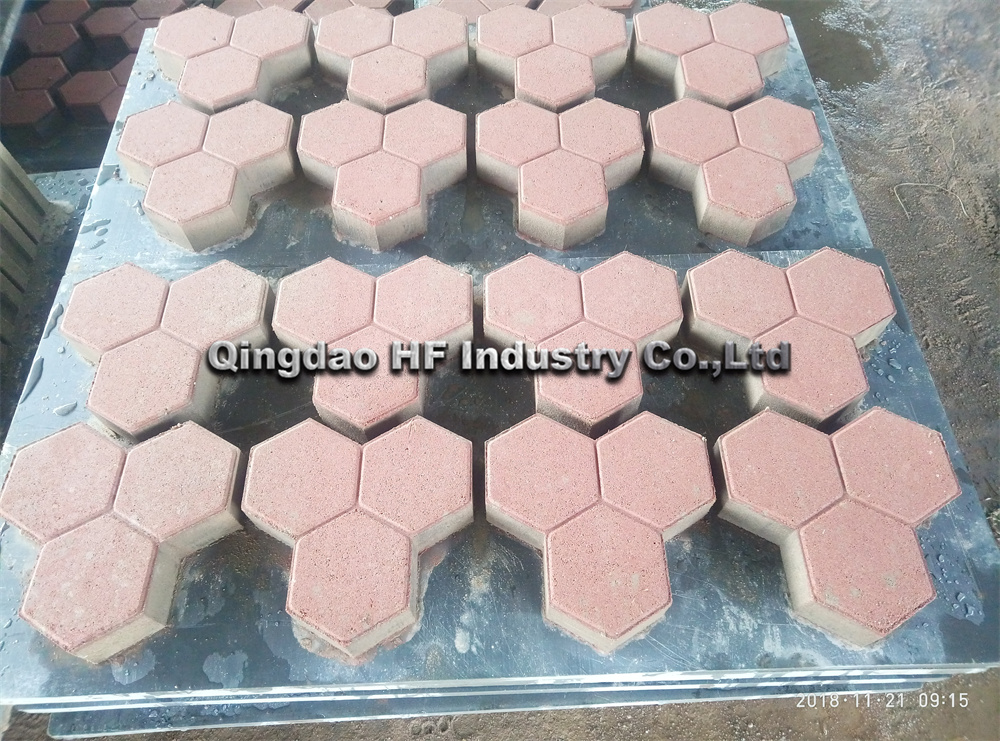

Labor practices in the brick manufacturing industry are another area of concern. In many developing countries, brick production is often associated with poor working conditions, low wages, and child labor. Workers in brick kilns may be exposed to hazardous materials and long hours without adequate safety measures. The informal nature of many brick-making operations makes it difficult to enforce labor laws, leading to exploitation.
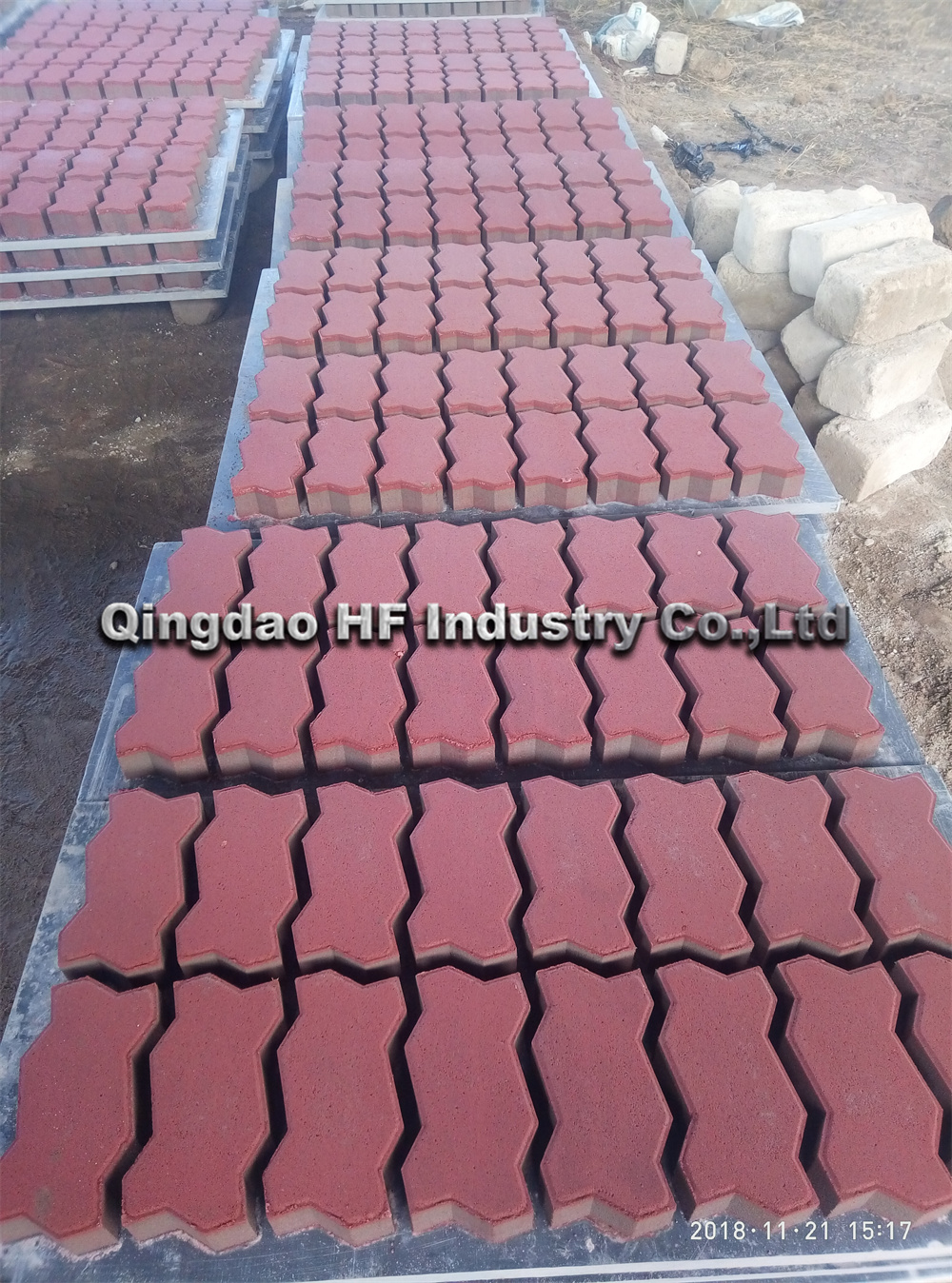

Additionally, the shift towards mechanization in brick manufacturing can displace traditional workers, creating economic challenges for communities that rely on manual brick-making techniques. While automation can improve efficiency and reduce costs, it also raises ethical questions about the treatment of workers and the future of traditional craftsmanship in the industry.
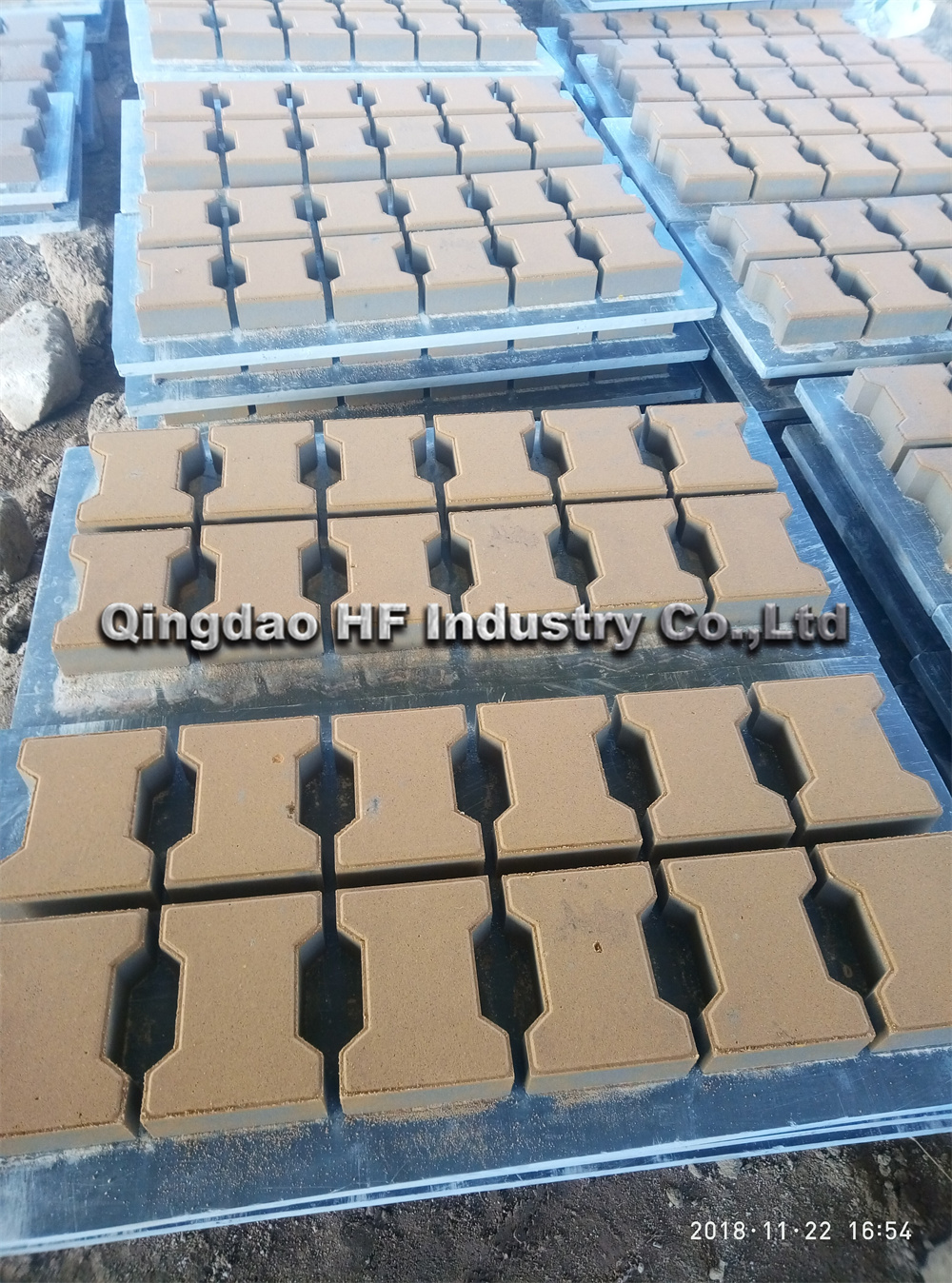

The brick manufacturing process has seen significant advancements in technology, but challenges remain. Traditional methods of brick production can be labor-intensive and time-consuming, leading to inefficiencies. While modern machinery can increase production speed and consistency, the initial investment in technology can be prohibitively expensive for small manufacturers.
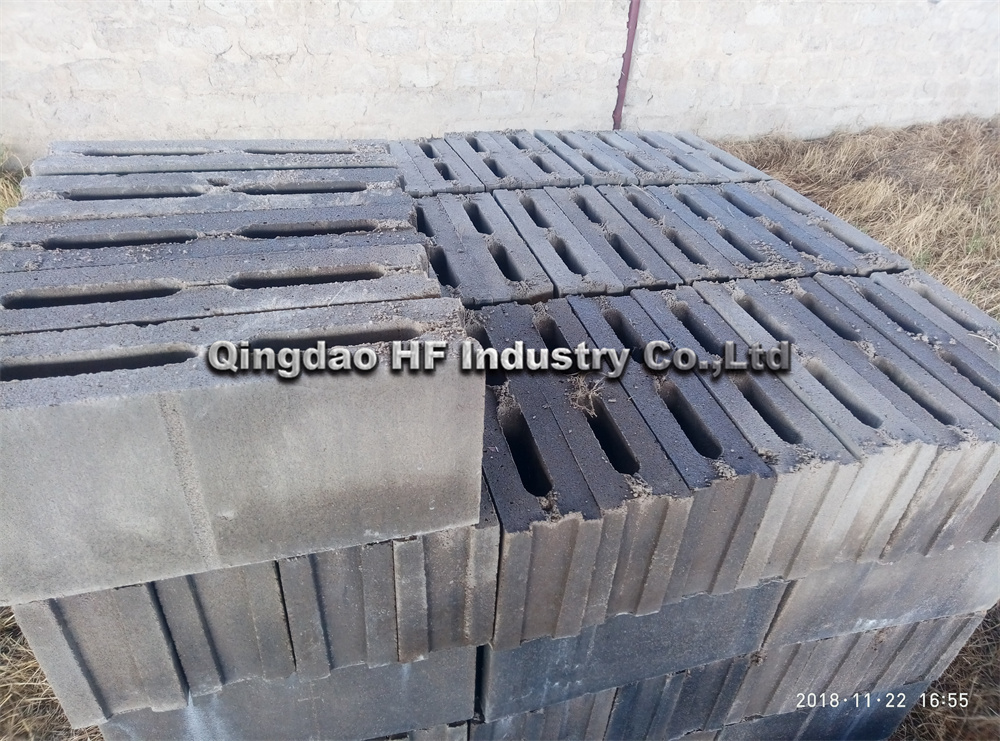

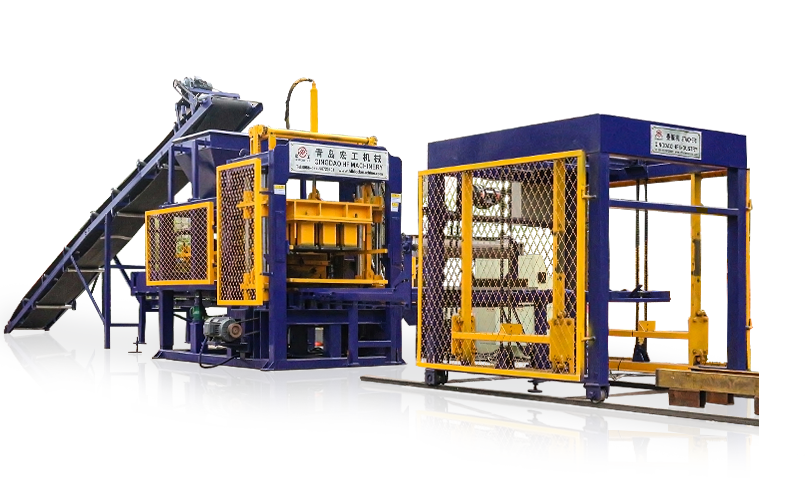
QT6-15 block making machinery full automatic is one machine with multifunction. Changing molds can produce various kinds of specification porous bricks, standard bricks, hollow bricks, with a double material-feeding machine can produce all kinds of thecolored road bricks, grassland bricks, and slope protection bricks etc.

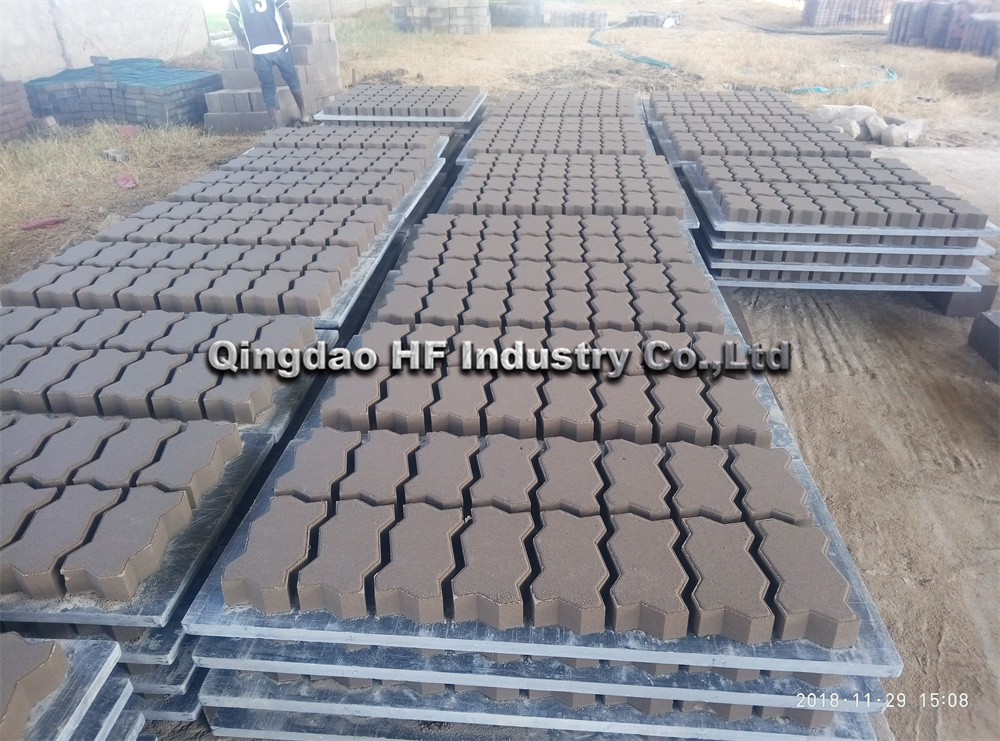
The brick manufacturing industry is also subject to market fluctuations that can impact profitability and sustainability. Economic downturns can lead to decreased demand for construction, resulting in overproduction and excess inventory. Conversely, during construction booms, manufacturers may struggle to keep up with demand, leading to rushed production and potential quality issues.


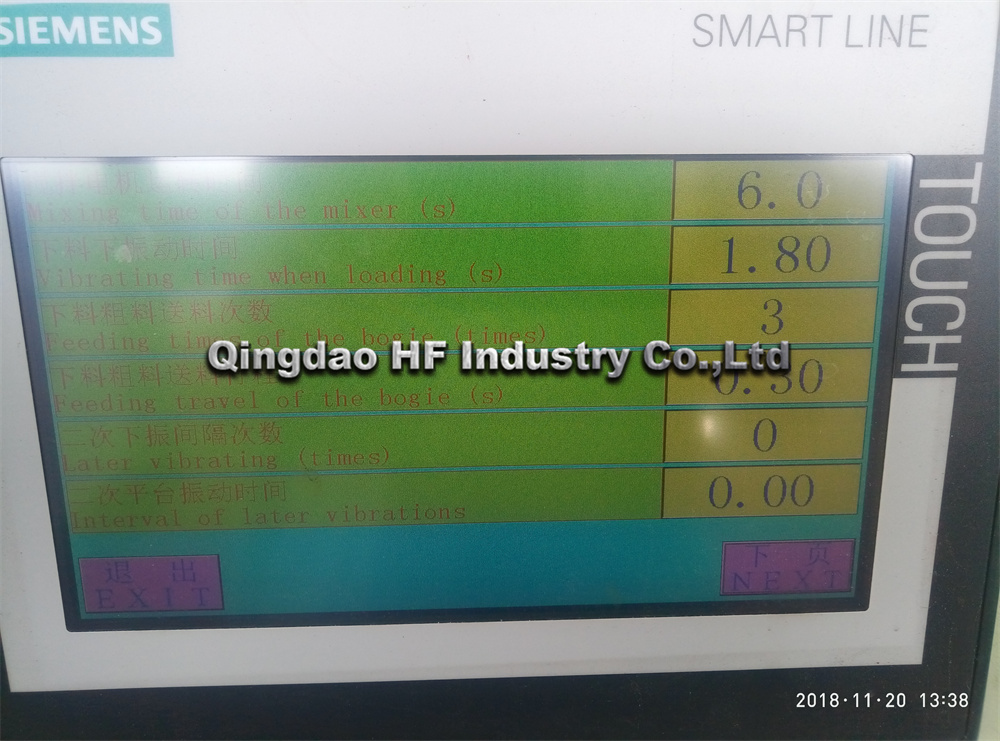
The Molding Vibration Block Machine has a short forming cycle and high production output. The continuous increase in vibration frequency during material feeding and forming vibrations reduces the feeding time by 3 to 4 seconds. The table vibration machine

A hollow block machine is a piece of industrial equipment specifically designed to produce hollow blocks, which are a type of concrete masonry unit (CMU) used in construction. These machines come in various sizes and capacities, and their primary function
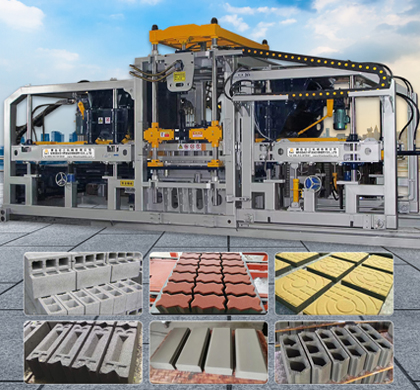
Concrete blocks are fundamental components in modern construction, providing the essential material for building walls, foundations, and various structures. The production of these blocks requires specialized machinery designed to mix, mold, and cure the
Whether for inquiries for inspections and
maintenance, for individual plant optimizations or
extensions, or spare and wear parts.

Our after-sales service is at your disposal for all
questions

Gemini Tower, Block B, Chunyang Road, Chengyang District, Qingdao, China
Show on the Map
We will contact you within 24 hours.